Example Integration
Let's detail how to integrate Tiep from start to finish via webhook. Tiep communicates with your Hospital
Information System (HIS) through a webhook endpoint that you expose.
Whenever a doctor saves a consultation, Tiep issues an HTTP POST request
against that URL with the structured consultation payload. Your HIS can then persist or act on
the payload automatically (store the consultation, schedule a follow-up, order imaging, and so on).
Step 1: create a facility
Any consultation must be associated to a facility. Create one as explained here.
Step 2: create a webhook
In the platform, navigate to Settings → Integration and provide the HTTPS endpoint that will receive webhook calls. Define a webhook secret (16 characters minimum) as Tiep uses it to sign every payload.
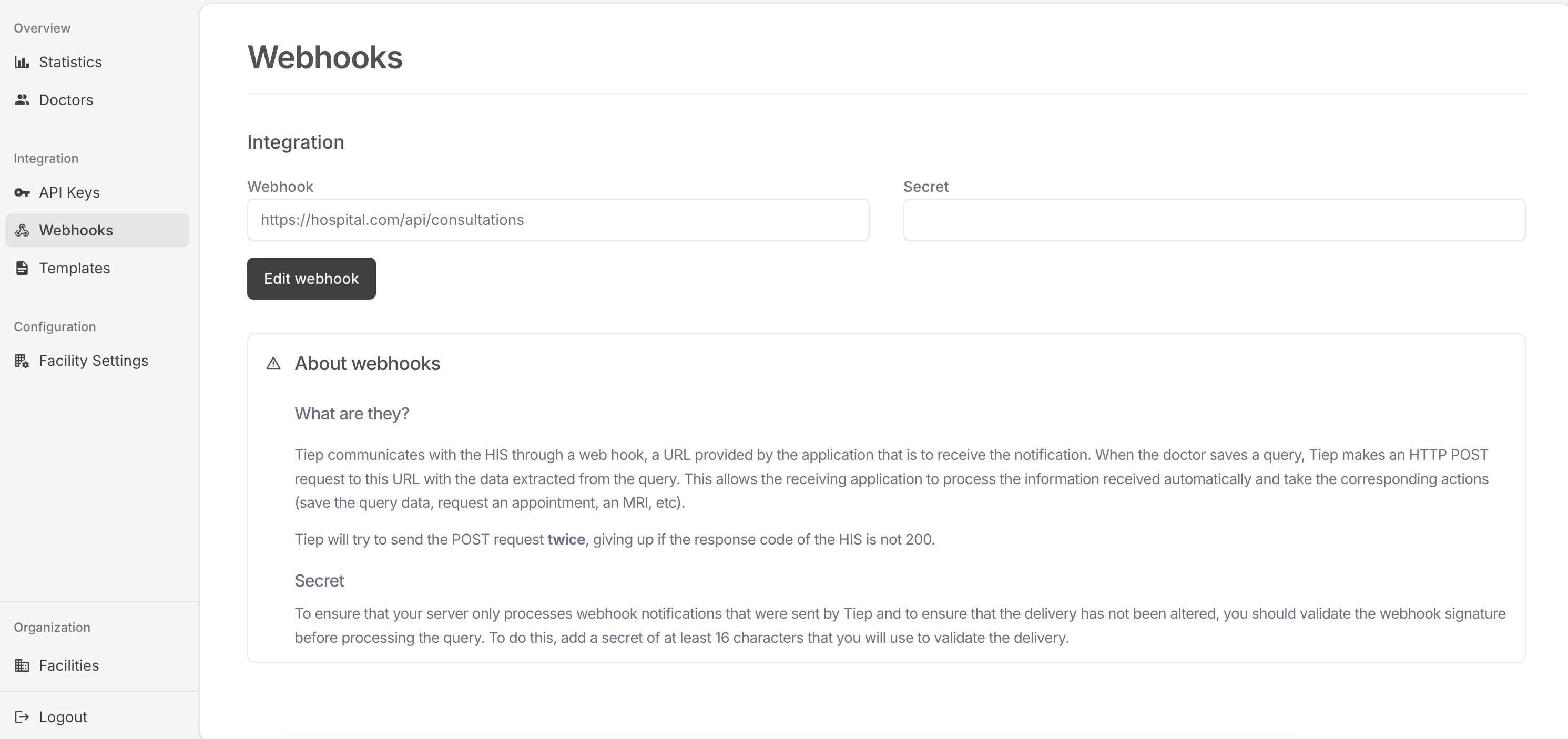
What is the webhook secret?
The secret lets you verify that inbound requests originated from Tiep and that no one tampered with them in transit. Use the same secret to recompute the hash when you receive an event. See Step 5 for a verification example.
Step 3: generate the launch URL
Doctors access the Tiep UI through a link generated by your HIS. Send a POST https://api.tiep.ai/v1/auth/generate-token
request containing the doctor's internal identifier, along create_session: true so you can poll
a session to see if it has finished, and the form you want to use
in the consultation. For instance:
{
"doctor_id": "1",
"create_session": true,
"form": {
"title": "Anamnesis",
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"reason-for-visit": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Reason for visit",
},
"pain-level": {
"title": "Pain level",
"type":"number",
"description": "Numeric scale from 1 to 10"
}
}
}
}
Tiep implicitly creates a doctor the first time if you didn't create it via the API.
You will receive a short-lived token that allows the physician to authenticate into Tiep (the token expires after 10 minutes):
{
"token": "qKaIW2jUWEFT841tP_vMYoswTAXiejtPgqf3sHQ90iY",
"session_id": "60c478df-2e8d-4317-90af-d801c217a034"
}
The final launch URL combines the token, the session id via &session_id=, and a &context= query parameter that contains patient metadata encoded
as URL-safe Base64 JSON.
The JSON payload must include a patient key. This is used to display a patient's name
in the UI. You can add any additional metadata you need; Tiep will echo it back inside the webhook payload. You may
include any HIS-specific metadata (session id, episode id, etc).
{
"patient": {
"resourceType": "Patient",
"identifier": [
{
"value": "123456"
}
],
"name": [
{
"use": "official",
"text": "John Smith"
}
]
},
"is_first_visit": true,
"consultation_id": 123,
"episode_id": 1838,
"any_other_key": "more metadata information"
}
Given the example above, the resulting link would look like:
https://app.tiep.ai/?token=qKaIW2jUWEFT841tP_vMYoswTAXiejtPgqf3sHQ90iY&session_id=7bee84ef-bd91-411e-b128-1f14c7a4555e&context=eyJwYXRpZW50IjogeyJyZXNvdXJjZVR5cGUiOiAiUGF0aWVudCIsICJpZGVudGlmaWVyIjogW3sidmFsdWUiOiAiMTIzNDU2In1dLCAibmFtZSI6IFt7InVzZSI6ICJvZmZpY2lhbCIsICJ0ZXh0IjogIkpvaG4gU21pdGgifV19LCAiaXNfZmlyc3RfdmlzaXQiOiB0cnVlLCAiY29uc3VsdGF0aW9uX2lkIjogMTIzLCAiYW55X290aGVyX2tleSI6ICJtb3JlIG1ldGFkYXRhIGluZm9ybWF0aW9uIn0=
Note you can pass in the intended language you want Tiep to run on via a query parameter lng=<LANG>
where LANG is an ISO 639 code. We currently support English (en), Spanish (es), Catalan (ca), French (fr), and Gallego (gl).
Consultations cannot be saved without context—always include the context parameter in the launch URL so the patient can be identified.
Here is how you could wire those pieces together in Python (replace API_KEY with the facility API key you generated earlier):
import json
from urllib.parse import urlencode
from base64 import urlsafe_b64encode
import requests
CONSULTATIONS_URL = "https://app.tiep.ai"
API_KEY = "2f32c3d709ff7db4ab43143ea477919d"
API_URL = "https://api.tiep.ai/v1"
def get_ephemeral_token(doctor_id: str):
res = requests.post(
f"{API_URL}/auth/generate-token",
json={"doctor_id": doctor_id, "create_session": True, "form": {
"title": "Anamnesis",
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"reason-for-visit": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Reason for visit",
},
"pain-level": {
"title": "Pain level",
"type":"number",
"description": "Numeric scale from 1 to 10"
}
}
}},
headers={"X-API-Key": API_KEY},
)
res.raise_for_status()
return res.json()
def generate_consultation_url(doctor_id: str, context):
token_in = get_ephemeral_token(doctor_id)
query_params = {
"session_id": token_in["session_id"],
"token": token_in["token"],
"context": urlsafe_b64encode(json.dumps(context).encode()),
}
return f"{PUBLIC_APP_URL}?{urlencode(query_params)}"
Step 4: run a consultation
Open the URL, run a consultation, and save it.
Step 5: receive the data
5. Receive the reports
Tiep issues a POST request to your webhook every time a consultation report is finalized. We retry the delivery once and stop if your endpoint does not return a 200 status code.
Each payload is signed with the webhook secret using an HMAC SHA-256 digest and sent in the X-Signature-256 header. The first thing your handler should do is recompute the signature and compare it against the provided value.
Keep the following in mind when validating webhook payloads:
- Tiep uses an HMAC hexadecimal digest.
- The signature always begins with
sha256=. - The digest is calculated with your webhook secret and the raw request body.
- If your language or framework enforces an encoding, ensure the raw body is treated as UTF-8.
- Avoid plain
==comparisons; prefer constant-time checks such ashmac.compare_digestorcrypto.timingSafeEqual.
Example
import hmac
import json
from hashlib import sha256
from django.http import JsonResponse
from django.utils.decorators import method_decorator
from django.views import View
from django.views.decorators.csrf import csrf_exempt
from his.models import Consultation
@method_decorator(csrf_exempt, name="dispatch")
class ConsultationWebhookView(View):
TOKEN = "MY-SECRET"
def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
received_signature = request.headers.get("x-signature-256")
expected_signature = f"sha256={hmac.new(self.TOKEN.encode(), msg=request.body, digestmod=sha256).hexdigest()}"
is_valid = hmac.compare_digest(received_signature, expected_signature)
if is_valid:
data = json.loads(request.body)
Consultation.objects.create(data=data)
return JsonResponse(
{"status": "success", "message": "Consultation received"},
status=200,
)
else:
return JsonResponse({"status": "error", "message": "Invalid signature"}, status=400)